Professional skills of intermediate wholesalers: Various techniques to preserve freshness
At Toyosu Market, we are making various efforts to deliver fresh fish to you.
Ike-jime/Shinkei-jime
Intermediate wholesalers handling live fish such as flounder or madai (red sea bream) at Toyosu Market use a technique called "ike-jime," a specific method of killing fish, in order to keep the "live" state (time until postmortem rigidity) as long as possible.
After making fish rest in a live fish tank *1, first, cut the part near the base of the gill with a knife in order to cut a part of the brain and the spine *2, then cut the lower half of the base of the caudal fin. This is done to destroy the hindbrain and kill it immediately, as well as to drain blood (bleeding) *3 and remove nerves *4. Nerve removal is a practice to stop the function of the spinal cord nerve, in which the spinal cord is destroyed by inserting something like a wire along the neural groove from the base of the caudal fin.
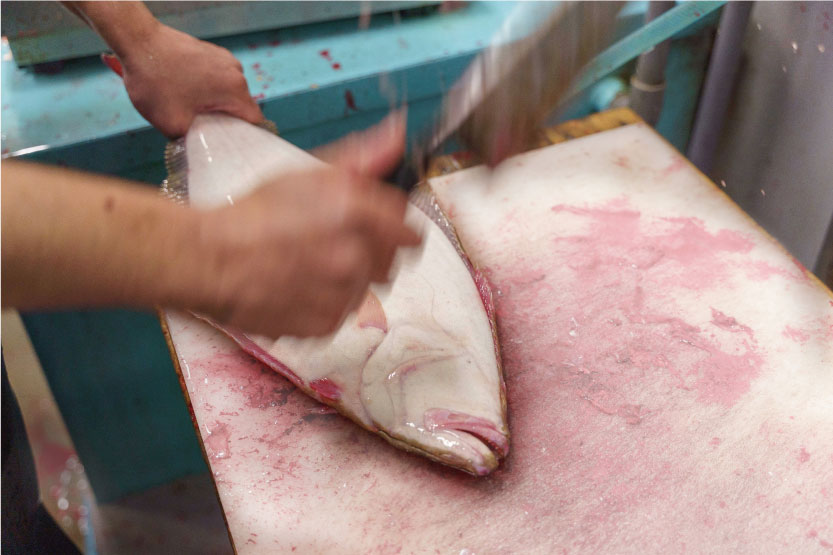

Flounder/Ike-jime
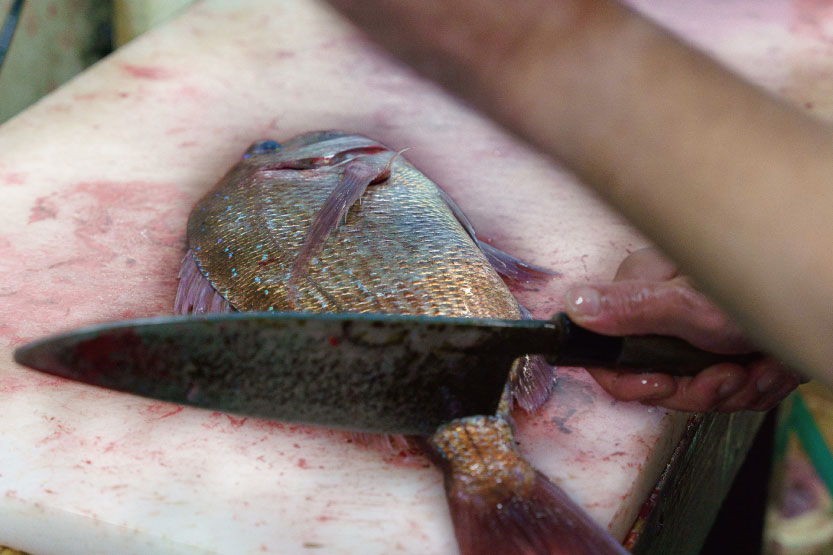

Madai/Ike-jime
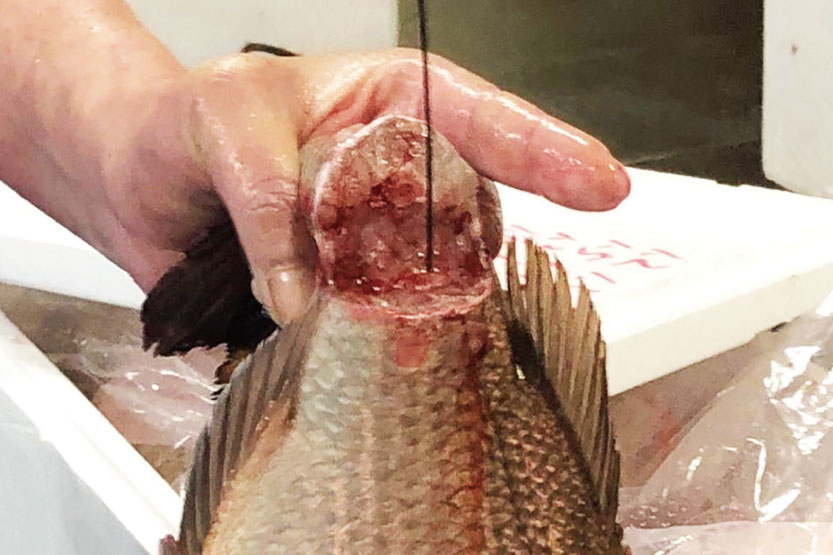

Madai/Shinkei-jime
*1: This is done to relieve stress experienced when they were caught (or during transportation) and return the amount of adenosine triphosphate (ATP [energy currency]) in the muscle to the normal state. After "ike-jime" is done, ATP in the muscle gradually decreases and rigidity progresses. After that, ATP disappears, and the fish becomes completely rigid. Inosinic acid, the source of fish's good taste, is produced by the decomposition of ATP; therefore, the process of rigidity is also the process in which the amount of inosinic acid increases.
*2: This is done to cut the blood vessels running at the lower edge (of the vertebral body) of the vertebral bone.
*3: This is done because blood causes a fishy smell.
*4: This is also called "shinkei-jime" because of this process; "shinkei" means "nerves" in Japanese.
After ike-jime, processed fish are stored at temperatures of 0 to 10 degrees Celsius; they are stored in a refrigerator until they become rigid, and after that, they are stored in ice. These storage methods have been found to be capable of delaying the starting time of rigidity and prolonging the time until complete rigidity.
Connoisseurs of salt-dried food
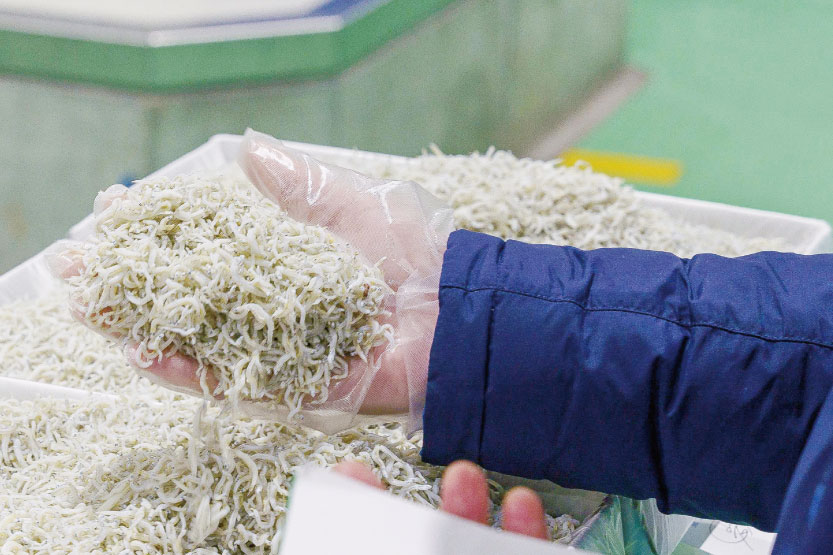

Shirasu (whitebait)
They take some shirasu in their hand to check its dryness and flavor, and whether there are any foreign substances.
Inventive packing methods
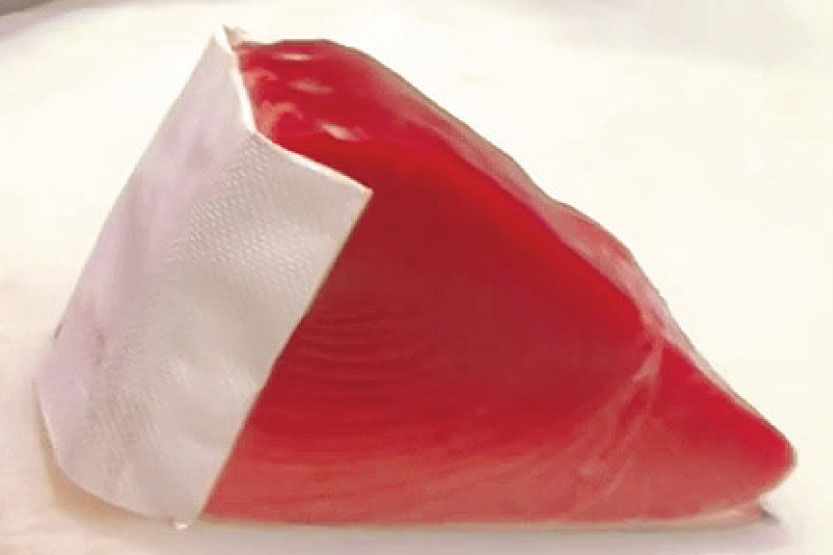

Paper
Tuna is usually carried in blocks and this often causes blood to seep from the chiai (part with most veins). To prevent this, tuna meat is wrapped up in a paper towel.
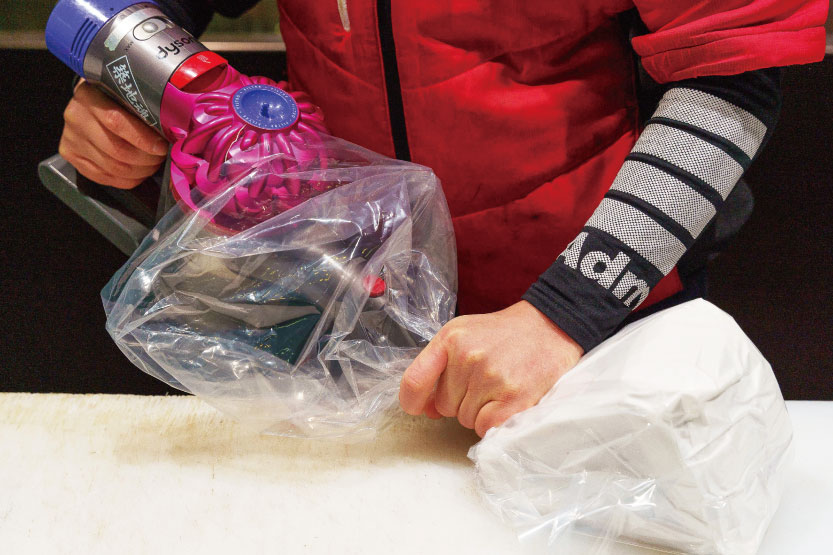

Removal of air
After putting it in a plastic bag, the air is removed to prevent oxidation and stop the tuna meat from cracking. This also enables tuna meat to be refrigerated efficiently.
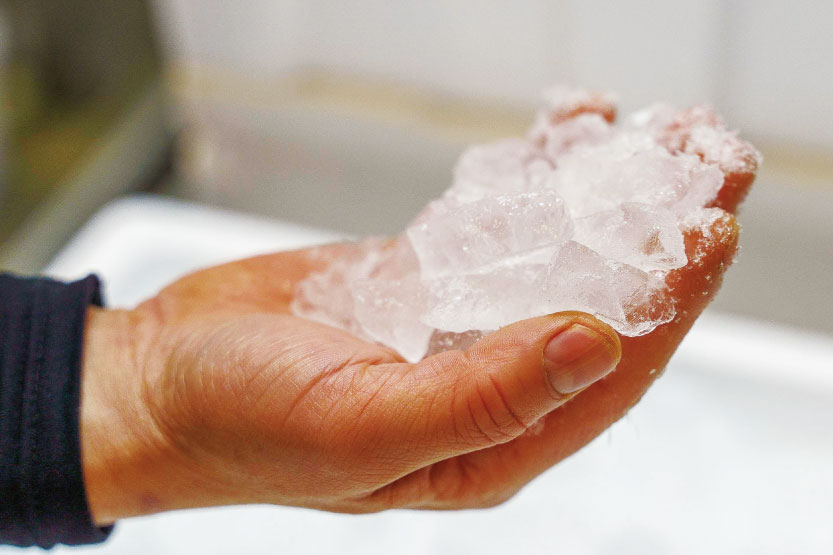

Ice
A fish box is filled with ice to keep the fish from moving. Tuna meat can be cooled better when put in fresh ice cubes, so they always use new ones.
Connoisseurs: Professional skills of intermediate wholesalers
Intermediate wholesalers evaluate marine products collected in the market from all over Japan and various parts of the world at auction or on a negotiation basis, and prepare ingredients that will adequately meet a wide variety of needs.
They have detailed knowledge on fish species, their sizes, production areas, seasonal delicacies, natural products, farm-raised products and their characteristics. Based on their many years of experience and achievements, they carefully inspect the products with the aim of providing the choicest marine products that will meet customer needs. Such roles are played by connoisseurs, professionals with a special eye for quality.
Oysters
Oysters arrive in various states.

Oysters with shells

Shucked oysters

Shucked oysters in a can

Packaged oysters
Oysters that have arrived from all over the country are sold by wholesalers according to the needs of the buyer; shucked oysters are sold as ingredients for hot pot cooking, oysters with shells for raw consumption, and so on.
When selling shucked oysters, they make sure to use a bowl or ladle, instead of touching them directly with their bare hands, to guarantee thorough hygiene management.

Oysters hitting retail shelves

Oysters scooped up with a bowl
Japanese horse mackerel
These fish have a wide variety of uses.

They arrive in greater volume than that of any other fresh fish.

Eyes, colors and width are checked.

Evaluated according to customer needs
Japanese horse mackerel arrive in greater volume than that of any other fresh fish. Japanese horse mackerel are sent to the market from all over the country throughout the year. There are differences in size, appearance, and the degree of fat depending on their production area and season. Wholesalers divide them according to customers' needs such as fish for sushi toppings, sashimi, salt-grilled dishes, fried dishes, and so on.
Japanese tiger prawn
Secret of keeping freshness and connoisseurs

Japanese tiger prawns being protected by a special sheet

Checking freshness

Divided according to weight in the tank
To prevent Japanese tiger prawns from being damaged during transportation, they are protected by a special sheet when delivered. When they provide Japanese tiger prawns to customers, they put special sheets and sawdust in a box in the same way for shipping them. *Before sending Japanese tiger prawns to customers, they pick up prawns and visually check their colors and sizes. They evaluate the prawns by their sense of touch and select actively moving ones with hard and stiff flesh.
*: In their natural setting, Japanese tiger prawns live in the sand; therefore, if they are put in a box with sawdust and a special sheet, a similar environment, they will relax and stay still.
Puffer fish
For security and safety

Arrive in a living state
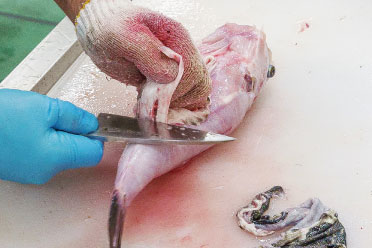
Cutting off the poisonous parts
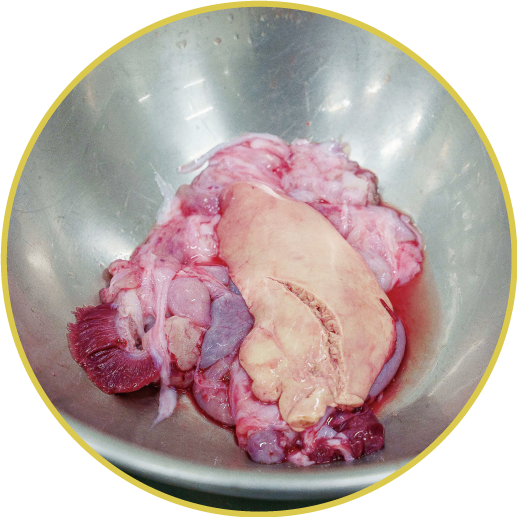
Poisonous parts

Locked freezing storage room
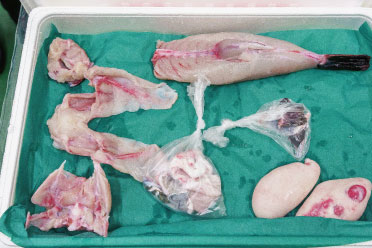
Poisonous parts of puffer fish flesh are completely removed
Since puffer fish are poisonous fish, they cannot be traded unless a licensed cook removes their poisonous parts for detoxification. Therefore, Toyosu Market has a facility called the "fugu-jodoku-jo," or pufferfish detoxification station, which is responsible for the management of poison. In this facility, safely separated poisonous parts are properly discarded after being stored in the freezing storage room. The flesh of pufferfish that have undergone such processes and had their poisonous parts completely removed are what appear on the market.
Fish Intermediate Wholesale Market

