Main Medical Benefit and related Programs
− CONTENTS −
②Children afflicted with designated chronic childhood diseases
③For children with disabilities
①For immature babies
Infants who are born with bodies that are not fully developed and who require hospitalization may receive medical care at public expense.
②Children afflicted with designated chronic pediatric diseases
If a child is diagnosed with one of the designated chronic pediatric conditions listed below, there is a system that helps reduce out-of-pocket medical expenses. In addition, the child may receive assistance for self-reliance (self-reliance support project) and benefits for equipment used in everyday life.
Malignant neoplasm, chronic kidney disease, chronic respiratory illness, chronic cardiac disease, endocrine disease, collagen disease, diabetes, inborn error of metabolism, blood disease, immunological disease, neurological/muscle disorder, chronic gastroenterological disease, disease accompanied by changes to chromosomes or genes, skin disease, systemic bone disease, vascular disease
* Information Center for Specific Pediatric Chronic Diseases (https://www.shouman.jp/)
③For children with disabilities
If a child receives therapy, such as surgery to mitigate the circumstances accompanying a physical disability, the child may receive medical care (self-reliance medical care) at public expense. Also, the child may be able to receive assistive equipment or benefits to pay for devices for everyday use.
In either case, there are limits that are dependent upon the severity of the illness, income and other factors. Consult with your municipality for details.
If a guardian experiences on unfortunate development (death or a serious disability), the mutual aid support system for ailments of disabled persons (voluntary enrollment) offers lifelong pension benefits to disabled children and persons. Inquire with your prefectural government or designated city.
Japan Obstetric Compensation System for Cerebral Palsy
If a baby delivered at a facility offering childbirth services and enrolled in the Japan Obstetric Compensation System for Cerebral Palsy develops severe cerebral palsy related to childbirth, and fulfills requirements such as those for weight at birth, fetus week number and severity of disability, compensation may be paid for nursing care, and the baby may be analyzed for the causes behind the symptoms of cerebral palsy.
Below is a list of facilities offering childbirth services that are enrolled in this program.
※ Obstetric Medical Compensation System(Japan Council for Quality Health‑care)
Note that the deadline for applying for compensation is the child's fifth birthday.
When you receive the "The Japan Obstetric Compensation System for Cerebral Palsy Certificate" from the childbirth facility, please keep the registration certificate carefully until your child turns 5 years old.
●For inquiries concerning the Japan Obstetric Compensation System for Cerebral Palsy
Japan Obstetric Compensation System for Cerebral Palsy Call Center
Tel. 0120-330-637
Hours: 9 a.m. – 5 p.m. (except weekends and holidays)
(except weekends and holidays, as well as year-end and New Year holidays.)
apan Obstetric Compensation System for Cerebral Palsy Symbol Mark
Child Illnesses and Injuries
− CONTENTS −
①Receiving an examination at a hospital or clinic
③Proper use of antibiotics (antimicrobial agents)
It is not uncommon for children to catch communicable diseases, get burned, become injured, drink something they shouldn't or experience other accidents. If a guardian who is usually around a child feels there is something different or unusual about the child, the guardian should closely observe the child. If necessary, contact your regular physician.
①Receiving an examination at a hospital or clinic
If you observe symptoms such as labored breathing, limpness, repeated vomiting, convulsions, loss of consciousness or the like, make sure to have the child examined at a medical facility. When receiving an examination, take notes about the child's symptoms, their changes and their duration. In addition, make sure to take this Maternal and Child Health Handbook, as it contains important records about the child.
②Children's Medical Hotline
(Tel: #8000 [an abbreviated dialing service you can call from anywhere in Japan])
If it is a holiday or at night, and you are unsure about how you should treat your child's symptoms or whether you should receive an examination at a hospital, you can call this hotline to obtain advice from a pediatrician or nurse on the proper way to treat the symptoms, information on hospitals where your child can receive an examination, and other useful advice. Please inquire for details to the local prefectural government office where you reside.
* Children's Medical Hotline #8000 (Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare)
*Child Emergency (Japan Pediatric Society)
③Proper use of antibiotics (antimicrobial agents)
Antibiotics, or antimicrobial agents, are medications to exterminate bacteria. They are not effective against viruses, which cause the common cold and influenza. In addition, the use of these medications can have side effects or can create bacteria against which antibiotics no longer work (also known as drug-resistant bacteria). 。
So that you can make an informed decision about whether or not to use antibiotics, if your child catches a cold, explain the symptoms in detail to your physician and ask any questions you may have. In addition, if the physician issues a prescription, make sure to administer the medication to your child according to the dosage and schedule indicated by the accompanying instructions.
* For more information about antimicrobial resistance (AMR), visit the AMR Clinical Reference Center website.
Preventing Accidents
− CONTENTS −
①Common Accidents According to Age
②A child seat can save a child's life
Children dying in unforeseen accidents has become a prominent issue recently in Japan. The types of accidents differ according to age, but the majority of them could have been prevented with proper attention provided by those around them. An important way to prevent accidents is to know in advance what kinds are prone to happen and when over the course of your child's development.
*"Protect Children from Accidents! Accident Prevention Handbook"
①Common Accidents According to Age
| Age | Common Accidents According to Age | Primary causes and preventive steps |
|---|---|---|
| Newborn |
Careless by those around children Suffocation |
☆An item is accidentally dropped down from above ☆Injury from a larger child hugging a smaller child hard or feeding something to the smaller child ☆Your child's face becomes buried in a soft pillow or futon mattress (Use firm infant bedding and have your baby lie on his or her back to sleep.) |
| 1-6 months |
Falling Burns |
☆Your child falls from a bed or sofas, baby carriers, and strollers (If possible, have your child sleep in a baby bed, not an adult sized bed, and put up the barrier when you are away from the bed.) ☆Spilling a hot drink on a child while holding the child. |
| 7-12 months |
Falling, collapsing, getting stuck Burns Near-drowning Accidental ingestion, poisoning Suffocation Injury in a motor vehicle |
☆Fingers or hands caught in doors or windows, or falls from doors, stairs, beds, strollers, or chairs. ☆Burns from an iron, hot water from a pot or electric kettle, steam from a rice cooker or humidifier ☆Drowning after falling into a bathtub or washing machine (Do not leave hot water in the tub after bathing.) ☆Accidental ingestion of cigarettes, medications, cosmetics, detergents, coins, button batteries, and magnets, etc. (Keep them out of children’s reach.) ☆A snack or other food like bread gets stuck in the throat ☆Falling from a car seat (Use a child seat.) |
| 1-4 years |
Accidental ingestion, poisoning Suffocation Falling, collapsing Injuries During Toothbrushing Burns Near-drowning Traffic accidents |
☆Your child has become more mobile, increasing the risk of accidental ingestion from a wider range of objects. ☆Foods like bread, sweets, beans, nuts, grapes, and cherry tomatoes cause choking ☆Falling from stairs, windows, veranda/balcony (Do not place items that would allow your child to climb up.) ☆Accidents caused by poking the throat with toothbrushes ☆Touching a hot pot, pulling a tablecloth and spilling hot water (Do not use a tablecloth.), fire from a lighter, matches, etc. (Do not place lighters or other flame-producing items within your child's reach.) ☆Drowning during bath time or while playing in the water ☆Traffic accidents from running out into the street (Walk while holding your child's hand.) |
(References)
◎Protect Children from Accidents! Accident Prevention Handbook" at the Children and Families Agency website provides information and tips on preventing accidents involving children.
*About the Child Accident Prevention Handbook (Children and Families Agency)
*Protect Children from Accidents! Accident Prevention Portal (Children and Families Agency)
Preventable injuries in children and countermeasures (Japan Pediatric Society)
◎At the Consumer Affairs Agency, tips and precautions for preventing accidents involving children are distributed via Child Safety Email newsletters and X (formerly Twitter).
・Child Safety Email newsletters and X information(The Consumer Affairs Agency)
・Consumer Affairs Agency "Protect Children from Accidents!"
* Information on Toothbrush Throat-Poking Accidents:
"Let's Develop a Habit of Brushing Teeth Fun and Safely" Leaflet (front) (the Japanese Society of Pediatric Dentistry)
"Let's Develop a Habit of Brushing Teeth Fun and Safely" Leaflet (back) (the Japanese Society of Pediatric Dentistry)
Use the contacts below for information and consultations concerning acute poisoning caused by chemical substances (tobacco, household items, etc.), medications, plants and animals. (Inquiries not accepted concerning accidental ingestion [pebbles, beads, etc.], food poisoning, chronic poisoning, or side effects from medications administered with the proper dosage.)
Japan Poison Information Center
Osaka Poisoning 110 Hotline:
Tel. 072-727-2499
(24 hours, 365 days)
Tsukuba Poisoning 110 Hotline:
Tel. 029-852-9999
(9 am – 9 pm, 365 days)
Tobacco Ingestion Accident Hotline
Tel. 072-726-9922
(Toll-free [provides tape-recorded information], 24 hours, 365 days, Information provided by automated voice response)
②A child seat can save a child's life
Under the law, children under the age of six must use a child seat. When your child rides with you in a car, put him or her in the child seat properly so you can protect your child's life and also prevent or mitigate harm from an accident. The likelihood of death or serious injury is considerably higher when not using a child seat compared to when you do use one. In addition, even if you use a child seat but the child is not fastened in properly or is sitting in an improper position, the seat's effectiveness declines considerably. Follow the instructions provided in the manual and use the child seat properly.
When a baby born at a hospital or clinic is discharged and returns home and rides in a car for the first time, make sure you have already prepared a child seat that conforms with national safety standards. You should make these arrangements before delivering a baby. In addition, make sure to keep the child seat fastened in a fixed position in a rear seat, if possible.
When your baby or toddler (a child under six years of age) rides with you in a car, you are obligated under the law to use a child seat, unless an exemption has been provided, for example if using a child seat would impair recovery from a medical condition.
Even for children over 6 years old, if their physique or other circumstances make it impossible to properly wear a seatbelt, use a child seat.
Initiatives Related to Child Seats – For the Sake of Precious Lives Yet to be Born –
Metropolitan Police Department Website "Child Seats to Protect Children"
Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism Website "Automobile Assessment"
Information on Child Seats
You can view a list of child seats and information about their safety from the following sources. Please use it to search for child seats.
Search for child seats (National Agency for Automotive Safety & Victims' Aid)
Child Seat Safety Comparison BOOK (National Agency for Automotive Safety & Victims' Aid)
③Dangers inside the car
Even outside of mid-summer, if the windows of a car are closed, the temperature inside can rise in a short time. A child inside the vehicle may become dehydrated or suffer a heat stroke. This is a life-threatening situation. There have also been accidents involving children using the equipment inside a car, so no matter how short a time it may be, never leave your child alone in the car. In addition, there have been accidents in which a child's neck or fingers were caught in a power window, causing serious injury. Before operating power windows, make sure to verbally inform your child. At other times, keep the windows locked.
④Bicycle dangers
When your child rides in a child seat on a bicycle, follow the rules of the road and take care to ride safely. Provide your child a bicycle helmet and fasten the seatbelt in their chair. Select a bicycle and child seat that is safe and conforms to standards, whether a regular bicycle, a power-assisted bicycle or a bicycle with two seats for children. In addition, it is easier for your bicycle to fall over when a child is riding, so never leave your child alone in a bicycle.
When riding a bicycle, wear a helmet to protect your life. Also, including those for children, use helmets marked with safety certifications.
* Bicycles Are Vehicles—Follow the Rules and Ride Safely(National Police Agency)
Correct use of child seats
When transporting a child under six years old, use a child seat correctly according to the instruction manual. Proper use reduces injury in an accident and prevents the child from interfering with driving.
 Use a seat that fits the child’s size and growth.
Use a seat that fits the child’s size and growth.
 Whenever possible, install it in a rear seat (if the front passenger seat has an airbag).
Whenever possible, install it in a rear seat (if the front passenger seat has an airbag).
 Securely fix the seat to the vehicle.
Securely fix the seat to the vehicle.
*If you must install it in the front passenger seat, move the seat as far back as possible and secure the child seat facing forward.
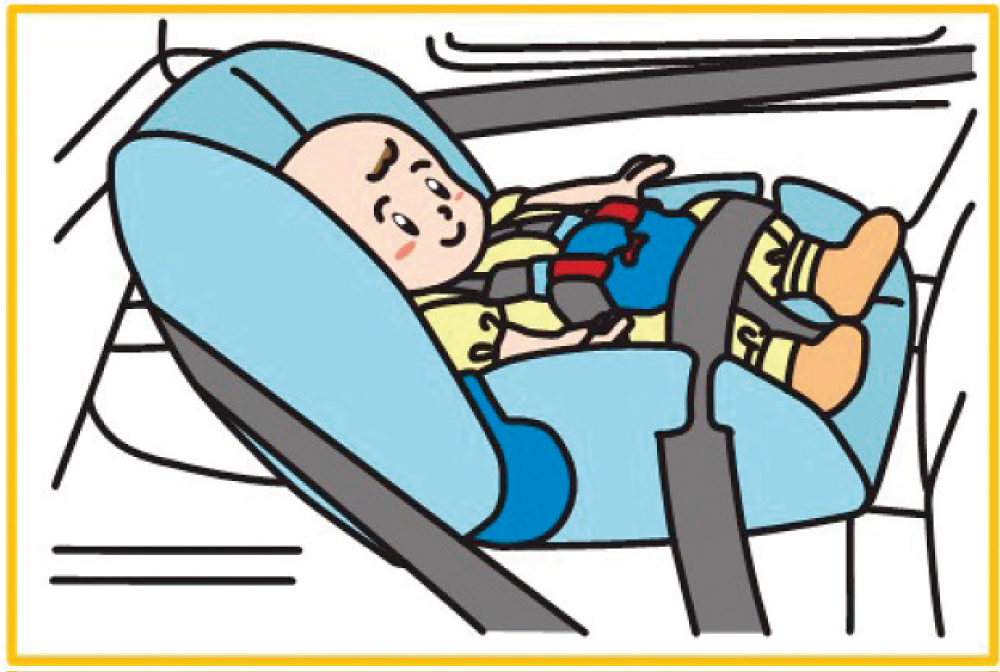

Infant seat

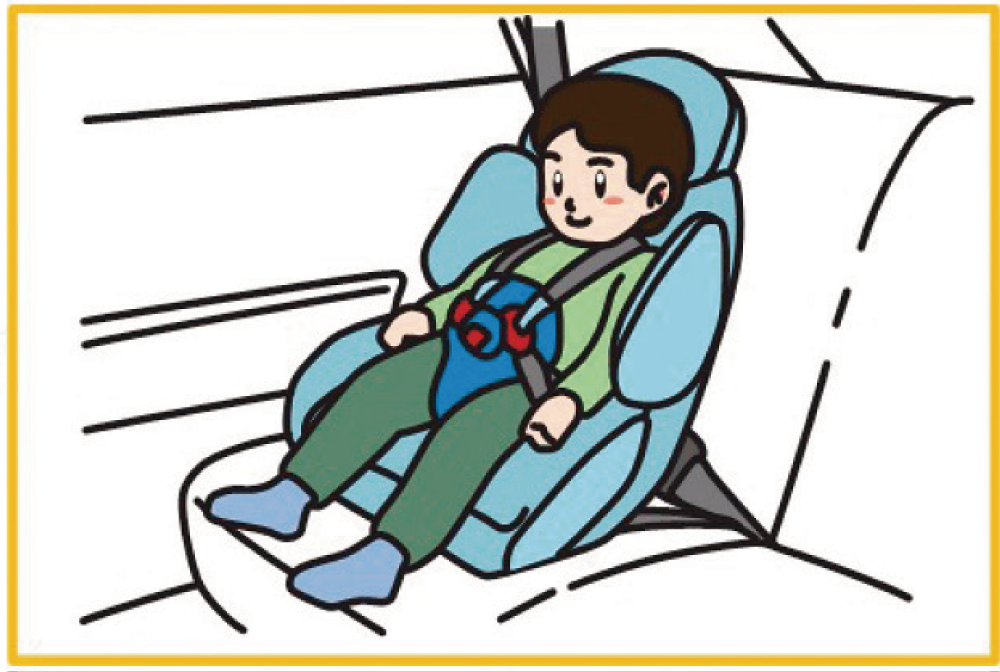
Toddler seat

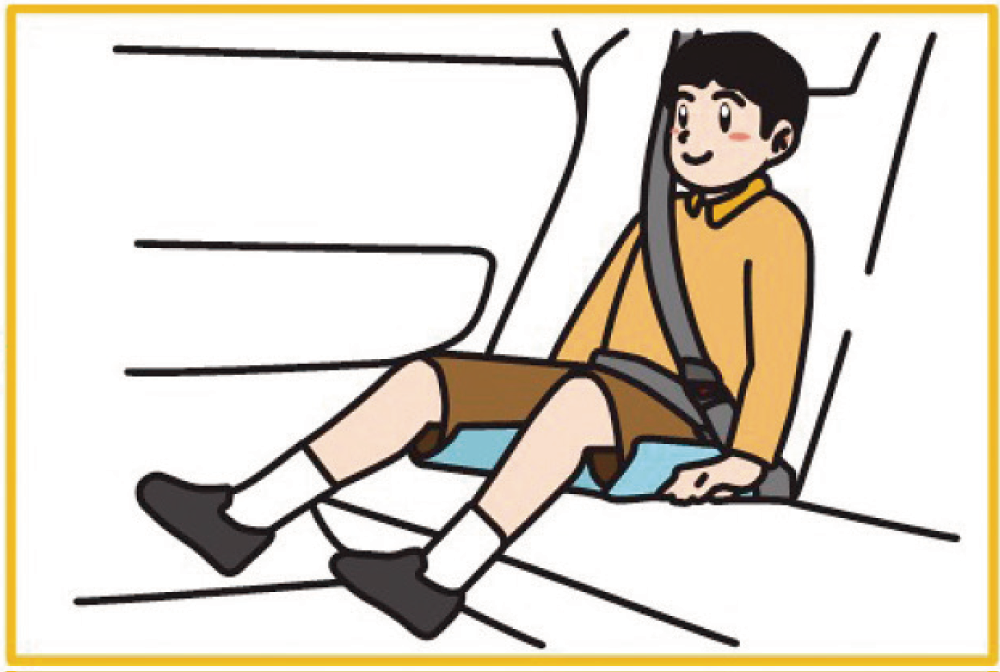
Booster seat
