For a Healthy Pregnancy and Childbirth
− CONTENTS −
①When you find out you are pregnant
③Everyday life during pregnancy
④Receive a health checkup or expert health guidance
⑧Dental and oral health management during pregnancy
⑨Protect your baby from the harms of tobacco and alcohol
⑩Avoiding communicable diseases during pregnancy
⑪For those who tested positive for hepatitis virus in the prenatal health examination
⑫Taking medication during pregnancy, after delivery and while breast-feeding
⑭Wearing a seatbelt during pregnancy
⑮Physical and psychological changes accompanying pregnancy and childbirth
⑯Your baby's regular physician
Pregnancy brings major physical and emotional changes as your baby grows. To stay healthy throughout this time, learn about ways to live and work safely while pregnant.
①When you find out you are pregnant
Look for a birth facility as early as possible.
Hospitals, clinics, and midwifery centres differ in the medical care, services, and costs they offer.
Picture the kind of birth you want, and choose a facility suited to your situation by considering access from your home or your family home, costs, and the availability of staff support.
The Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare’s “Shussan Navi” lets you narrow your search by region and detailed criteria and check each facility’s information, midwifery care, ancillary services, and costs. Make good use of it.
*Shussan Navi (Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare)
②Support during pregnancy
Your municipality offers accompanied consultation support during pregnancy.
These consultations help all expectant mothers and families plan for pregnancy, birth, and childcare, ease anxieties, and confirm available services and supports. Public‑health nurses, midwives, or other trained staff handle the interviews, providing expert information on pregnancy and childbirth.
Interviews are held when you file your pregnancy notification, in late pregnancy, and after delivery, but you can seek advice at any time during or after pregnancy. Because methods and timing differ by municipality, check with your municipal office when you submit the pregnancy notification or if you move.
③Everyday life during pregnancy
A pregnant mother will experience various changes as the baby in her body develops. Please be aware of how you go about your work or take breaks (for example, by resting on your side even for short spells while doing household chores or at work), how you eat, and so on. You should be more attentive than usual to your health. Contact your obstetric medical facility immediately if you experience vaginal bleeding, a bloated stomach, or abdominal pain; if your water breaks; or if your baby's movements are weak or have stopped.
f you notice any other troubling symptoms, don’t keep them to yourself and seek advice.
④Receive a health checkup or expert health guidance
During pregnancy, even if there are no particular concerns, it's important to undergo prenatal health examinations to check on the fetus's growth and your own health condition (such as blood pressure and urine). Municipalities provide subsidies for the cost of these health examinations.
To have a safe and healthy delivery, you need to be careful about your everyday routine, nutrition, environment and many other things. Make sure to follow the advice provided by your physician, dentist, midwife, public health nurse, dental hygienist, dietician and or other medical professional. If you have any worries or concerns about pregnancy or delivery, or you experience stress at home or at work, do not hesitate to consult with these professionals. Maternity classes and parenting classes also provide useful information.
If you return to your parents' home before or after delivery (or to give birth there), contact a childbirth facility there as soon as possible and consult with the maternal and child health official in the municipality where you or your parents live.
* Pregnancy abnormalities (illnesses) like those listed below may be discovered during a health checkup for expectant mothers.
• Miscarriage: This is when pregnancy terminates before the end of the 22nd week of pregnancy. Symptoms may include vaginal bleeding and lower abdominal pain. Even if there is no particular cause for miscarriage in the early stage of pregnancy, it occurs with approximately 10% to 15% of pregnancies. If you experience miscarriage two or more times, you may require a test or treatment.
• Anemia: During pregnancy, you may experience anemia due to thin blood. To prepare for delivery, you should consume a large amount of iron. Severe anemia requires treatment.
• Threatened preterm labor: This is when there is a possibility of going into labor sooner than the normal time (before the 37th week of pregnancy). Symptoms include lower abdominal pain, vaginal bleeding or your water breaking early. In this case, you will be prescribed a regimen of rest, medication and so on.
• Gestational diabetes: This condition resembles diabetes, and it can happen even if you've never been diagnosed with diabetes before. In the case of gestational diabetes, you must follow a certain dietary regimen and manage your blood sugar.
• Preeclampsia (gestational toxicosis): A condition characterized by high blood pressure and the presence of protein in the urine.. Be aware that the condition may suddenly worsen, with symptoms such as severe headaches or eye irritation.
Placenta previa: The placenta is in a lower position than normal and is blocking the cervical opening. The condition may be accompanied by massive bleeding. A Cesarean section is required during delivery.
Abnormal volume of amniotic fluid: The placenta, which supplies the baby with oxygen and nutrition, disconnects from the uterus prior to delivery. Since the baby will have insufficient oxygen, emergency delivery may be required. The primary symptoms are abdominal pain and vaginal bleeding, and may also include diminished fetal movement.
⑤Risks during pregnancy
If any of the following apply to you, then you are at high risk of experiencing an abnormality (or illness) during normal pregnancy or child delivery. If you have any worries, consult with a physician at a hospital or clinic.
Young of age (under 20), of advanced age for an expectant mother (age 35 or older), low height (under 150 centimeters), overweight (BMI 25 or higher), drinking alcohol, smoking, pregnant with multiple fetuses, giving birth with fertility treatment, afflicted with diseases such as diabetes or kidney disease, experienced problems with past pregnancy or delivery
⑥Rest during pregnancy
Getting enough rest and sleep is essential while pregnant. Adequate downtime helps you recover from fatigue, reduces stress, and keeps both mind and body stable throughout pregnancy.
If morning sickness is severe or you can’t sleep well at night, find spare moments to lie down or simply close your eyes. Use cushions or pillows so you can rest in whatever position feels most comfortable.
⑦Exercise during pregnancy
Staying active helps build stamina for delivery and the postpartum period and aids in weight management. Exercise within your limits, according to your condition each day. Some women with complications should avoid exercise, so always consult your doctor before starting.
Recommended activities include light aerobic exercises such as walking or prenatal yoga—aim for an intensity where you can still carry on a normal conversation. Avoid sports with a high risk of falling or vigorous movements that could press on your abdomen.
⑧Dental and oral health management during pregnancy
During pregnancy, it may become difficult to thoroughly brush your teeth due to physical changes such as morning sickness, and your hormonal balance and diet may also change. Therefore, this is a time that is prone to gum disease and cavities. During the morning sickness phase, try to brush your teeth when you’re feeling well, and if brushing is too difficult, rinse your mouth regularly.
To keep the inside of your mouth clean, in addition to your regular oral care, arrange to have your teeth and mouth cleaned with routine dental checkups and, if necessary, receive dental treatment during stable periods of your pregnancy (around the fourth to eighth months). Keeping your teeth and mouth healthy is important for both you and your baby. Staying conscious of dental and gum care will help you spend your pregnancy with greater peace of mind.
※ Q & A on dental care during pregnancy (Perinatal Oral Care Promotion Committee)
⑨Protect your baby from the harms of tobacco and alcohol
Smoking during pregnancy hightens the risk of threatened preterm labor, early breaking of your water and abnormal volume of amniotic fluid, thereby having a negative effect on the fetus' development. It is also said that smoking is one of the risk factors for sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS). Studies show that if someone smokes around an infant, the risk of SIDS increases. A pregnant woman’s own smoking, as well as passive smoking from others around her, can also be a contributing factor to SIDS after birth. All adults involved in a child’s life should quit smoking.
In addition, alcohol can have a deleterious effect on the fetus' development (particularly brain development). Do not drink alcohol anytime during pregnancy. Even after delivery, you should refrain from drinking alcohol while you are still breast-feeding your baby.
⑩Avoiding communicable diseases during pregnancy
During pregnancy, immunity is reduced, making you more susceptible to communicable diseases. You may also be unable to take effective drugs during pregnancy out of concern for their effect on the baby. Wash your hands regularly, and also gargle and take other such measures to prevent infection.
If some sort of microbe (such as bacteria or a virus) is transmitted from the mother to the baby, in rare cases it could have an effect on the baby. A health checkup for expectant mothers can also check for the presence of communicable diseases. You can also receive treatment to prevent your baby from becoming infected, so you should make sure to receive an examination.
If you contract erythema infectiosum (fifth disease) during pregnancy, it can increase the risk of miscarriage. If you develop a rash after fever or fatigue—or have other symptoms that suggest fifth disease—consult a medical facility. Because infection can be asymptomatic, tell your doctor at prenatal check‑ups if anyone around you has fifth disease. Avoid contact with people who have cold‑like symptoms as much as possible, and practise basic infection prevention such as hand‑washing and wearing a mask.
Some mother‑to‑child infections can be prevented with daily precautions. For example, to prevent cytomegalovirus infection, wash your hands thoroughly after contact with a child’s saliva or urine. To prevent toxoplasmosis, cook meat thoroughly, avoid contact with stray cats, wear gloves when cleaning a pet cat’s litter box or gardening, and wash your hands afterward.
* National Institute of Infectious Diseases
* Prevent Infection of Babies and Mothers
※ Erythema infectiosum (Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare)
⑪ For those who tested positive for hepatitis virus in the prenatal health examination
If you test positive (+) for HBs antigen, it means you are infected with the Hepatitis B virus. Similarly, a positive (+) result for HCV antibodies indicates an infection with the Hepatitis C virus. In both cases, you might not experience any symptoms, yet there's a possibility of developing hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, or liver cancer in the future. It's crucial to see a doctor and undergo detailed examinations.
You may be eligible for subsidies for the initial detailed examination, regular check-ups, and treatment of hepatitis. Please consult with your prefecture or the liver disease consultation and support center for more information.
※ The Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare's website also provides details on these subsidies.
⑫Taking medication during pregnancy, after delivery and while breast-feeding
If you are going to take medication while pregnant or breast-feeding, make sure to speak with a physician, dentist or pharmacist. Since it is dangerous to stop taking medication or to change the way you take it or the dosage without consulting a health professional, make sure you closely follow your physician's instructions for how to take your medication and in what amount.
* Pregnancy and Medication (Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare)
* The National Center for Child Health and Development provides information on taking medication while pregnant, so speak with your regular physician about it.
* The Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency(PMDA) website has a search feature so you can search for the package inserts of individual medications.
* Search for information on package inserts for prescription drugs (The Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency)
In addition, before receiving a uterotonic or other such medication used during childbirth, make sure to receive a thorough explanation from a physician on its necessity, the effects, the side effects and so on.
Your and Your Baby’s Health Info
Protecting Your Baby from RSV Infections
Starting in 2024, to prevent upper respiratory infections caused by RSV (Respiratory Syncytial Virus), which commonly infects newborns and infants, it is now possible for mothers to receive a vaccine in late pregnancy. This helps protect their babies from infection or prevent severe illness after birth. Please note that this vaccine is not covered by insurance.
If you are interested, please consult a medical institution.
⑬Painless childbirth
During vaginal delivery, anesthetics can be used to alleviate the pain of contractions
If you're considering painless childbirth, check the website provided below or otherwise gain a solid understanding of how your hospital or clinic handles this procedure. Then speak with your physician to select a delivery method.
The Right Way to Wear a Seatbelt When Pregnant
Wearing a seatbelt properly helps protect both the mother and the baby from injury in the event of a car accident. However, for health reasons, consult your doctor to ensure that wearing a seatbelt is appropriate for your condition.
 Wear both the lap belt and the shoulder belt.
Wear both the lap belt and the shoulder belt.
 The shoulder belt should not go across the neck.
The shoulder belt should not go across the neck.
 Position the shoulder belt between the breasts and off to the side of the belly.
Position the shoulder belt between the breasts and off to the side of the belly.
 Place the lap belt below the belly, as low as possible across the hips and pelvis.
Place the lap belt below the belly, as low as possible across the hips and pelvis.
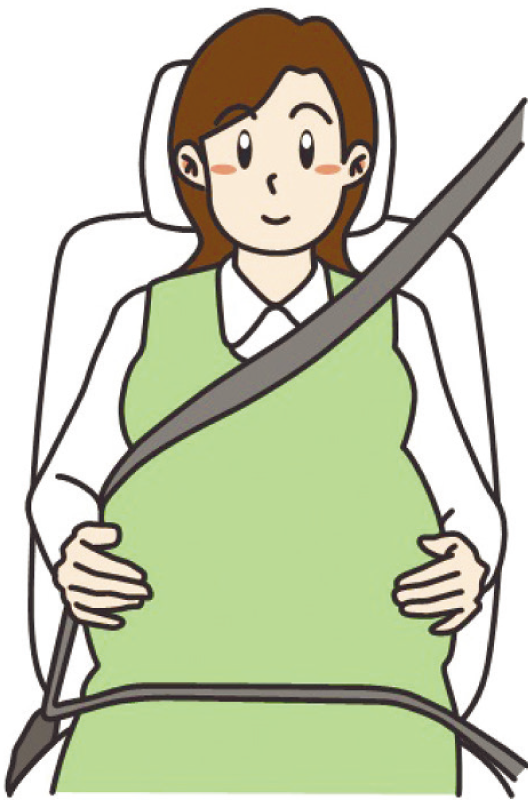
⑭Wearing a seatbelt during pregnancy
When driving during pregnancy, avoid driving yourself as much as possible if you are experiencing morning sickness, feeling unwell, excessively drowsy, or are in the later stages of pregnancy when your belly has grown larger.
Wearing a seatbelt is a legal requirement in any seat of a motor vehicle, including the rear seats. Even if you are pregnant, wearing a seatbelt properly can protect you and your baby from harm in the event of a traffic accident. However, since each pregnancy is different, confirm with a physician on whether wearing a seatbelt will be detrimental to your health.
To reduce the effect on the fetus during an accident, while you are pregnant, where a seatbelt not only over your lap, but also over your shoulder. Make sure to fasten the seatbelt properly so that it is not pushing into your enlarged belly.
During pregnancy, blood clots (thrombi) are more likely to form inside your blood vessels, which can lodge in veins in the legs or block major vessels such as those in the lungs (venous thromboembolism).
If you stay still for long periods while travelling, this risk can increase further. On long journeys, take frequent breaks, drink plenty of fluids, and move your legs regularly.
* ' The Right Way to Wear a Seatbelt When Pregnant ' (Tokyo Metropolitan Police Department)
⑮Physical and psychological changes accompanying pregnancy and childbirth
You may be worried by changes in your body and lifestyle caused by pregnancy and childbirth. In particular, after childbirth, you may feel down, cry easily or feel uncertain. In many cases, this is a temporary thing, but feelings of unhappiness or panic, or uncertainty about raising a child, may continue for two weeks or longer. Postpartum depression reportedly occurs in 10% to 15% of mothers after childbirth. After childbirth, a mother tends to focus on her baby, which can hinder her recovery from an abnormal physical and mental state. In addition, the father and other people around the mother will tend to make the baby their first priority and overlook changes in the mother. If you feel uncertain during pregnancy or after childbirth, or you wonder whether you are experiencing postpartum depression, do not worry in solitude. Consult with a physician, midwife, public health nurses at children and family centers, local child-rearing consultation organizations, or consider taking advantage of services such as postnatal care.
Postnatal care involves support for the mother's physical and mental well-being, parenting support, and assistance with breastfeeding, among other services.
Also, if you feel unusual during pregnancy or childbirth, you may require continued treatment or medical examinations after childbirth. Even if you think you are making good progress, receive an examination by a doctor just in case.
⑯Your baby's regular physician
To feel more at ease raising your baby after birth, it’s a good idea to choose a regular pediatrician during pregnancy—someone you can consult about your child’s health whenever needed.
They become a reliable support during childcare, helping with illness, injuries, vaccinations, and more.
⑰Using the Maternity Mark
The maternity mark is something worn by pregnant and postpartum women on public transportation, workplaces, restaurants, and other places to help those around them show consideration. It also makes it easier to identify pregnant or postpartum women during emergencies or disasters.
