Baby's Development
Newborn characteristics
A baby within the first 28 days of life is considered a newborn. This period involves significant bodily adjustments as the infant acclimatizes to life outside the womb. Their immune systems are still developing, necessitating careful attention to their needs through informed care and affection.
●Weight and Height
It's normal for newborns to experience physiological weight loss, shedding up to 10% of their birth weight within the first 4 to 5 days due to a higher volume of urine output compared to fluid intake. This is not a cause for concern; babies typically regain their birth weight about a week after birth.
●Breathing and Heart Rate
A newborn's breathing rate averages 42 to 45 breaths per minute, and their heart rate ranges from 120 to 140 beats per minute. Both rates can increase with activities as mild as crying or feeding.
●Body Temperature
The normal body temperature for a baby is about 36.5 to 37 degrees Celsius. Minor fluctuations above 37 degrees are not alarming. Newborns have yet to fully develop their ability to regulate body temperature, making them sensitive to environmental changes. Therefore, it's important to maintain a comfortable room temperature and adjust clothing and bedding accordingly to keep your baby comfortable.
●Symptoms specific to newborns
• The head may be deformed due to passing through the birth canal, but this will heal within a few days.
• A bump on the head 2-3 days post-birth is common. It often fades naturally within a few weeks due to the pressures experienced during delivery.
•Neonatal jaundice, causing yellowing of the skin, appears around 3 to 4 days post-birth and usually clears up on its own within 1 to 2 weeks. Similarly, any peeling of the skin is temporary and should improve within a week.
●Newborn Reflexes
Stimulation of the lips triggers sucking motions; stimulation around the mouth incites following movements. Turning the baby's head to one side results in limb extension on that side, a phenomenon known as the Moro reflex. Startle responses to sound or light, involving trembling and limb extension, are typical reflex actions.
Signs Warranting Medical Consultation for Newborns
・Persistent body temperature exceeding 37.5 degrees Celsius.
・The appearance of cyanosis, a purplish tint to lips and skin, which can occur briefly under certain conditions like after intense crying or sleeping in an awkward position.
・When severe jaundice is observed
・Regular vomiting of breast milk.
・Daily diarrhea
・Constipation persisting for more than three days.
・Severe inflammation or sores around the navel or on the skin.
・Other symptoms include strange crying, lack of energy, and crying violently when moving limbs.
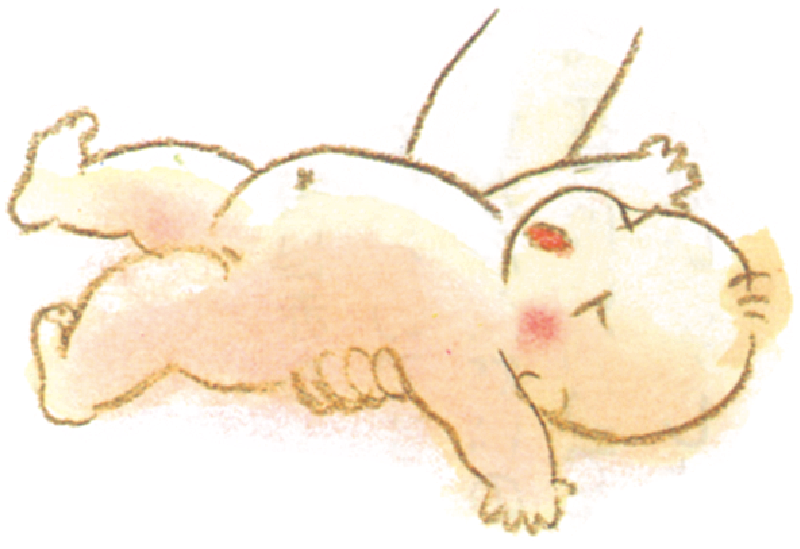
Newborn reflex movements
Sucking Reflex
An instinctive reaction where newborns attempt to suck anything that touches their lips, aiding in breastfeeding initiation.

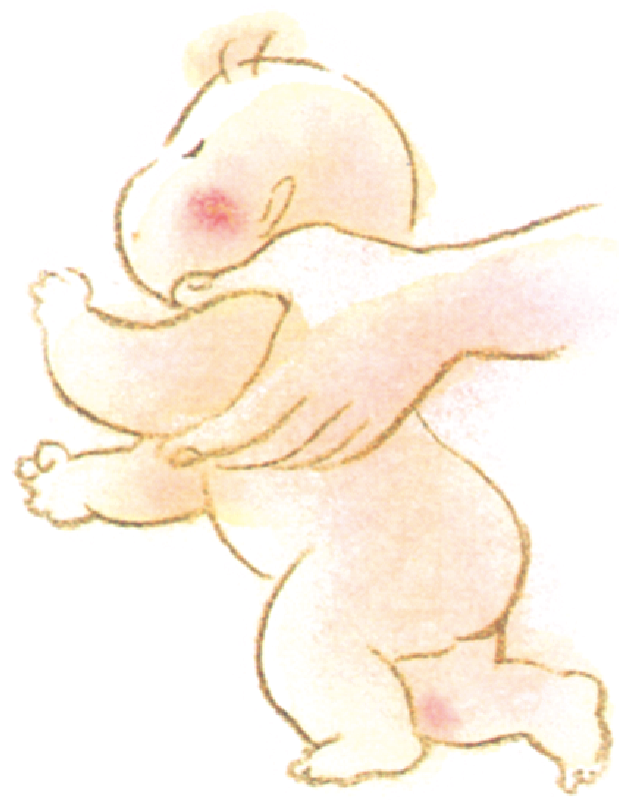
Automatic walking movement
When supported under the armpits and slightly leaned forward, newborns display stepping motions.

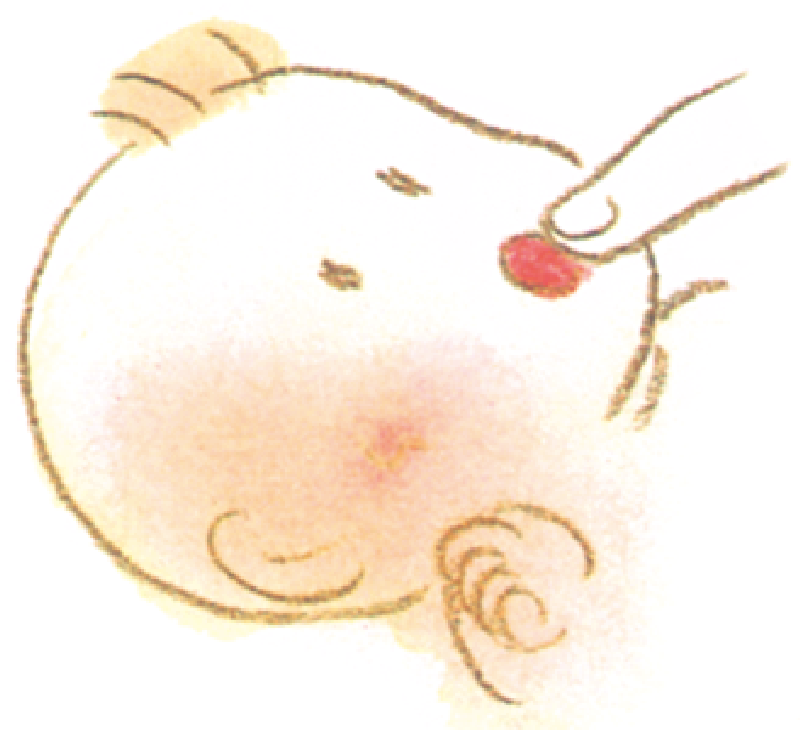
Foot grip reflex
Stimulation of the foot soles causes bending of thighs and knees, pulling the feet together.
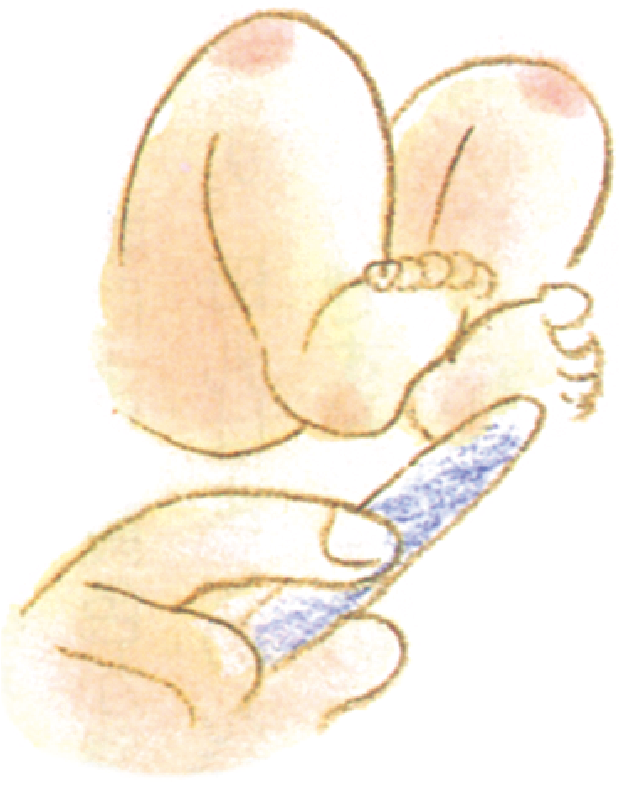
Hand grip reflex
The baby will clasp tightly around anything that comes into contact with their palm.
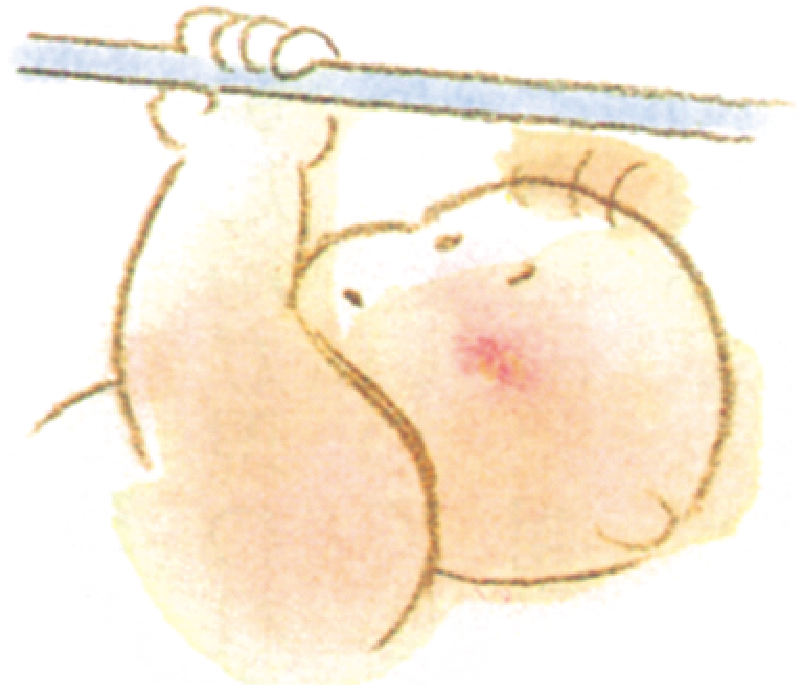

Moro reflex
Exposure to sudden light or sound leads to spreading of arms and tremulous motions.

Baby exercise
Engagement with both parents fosters mental and physical development. Beyond vocal interaction and comfort, physical touch and gentle exercise are necessary.
From 2 months, as your baby becomes more active and their neck strengthens, encourage tummy time or support their limbs for movement. Ensuring exercises are aligned with your baby’s natural limb movements is key.
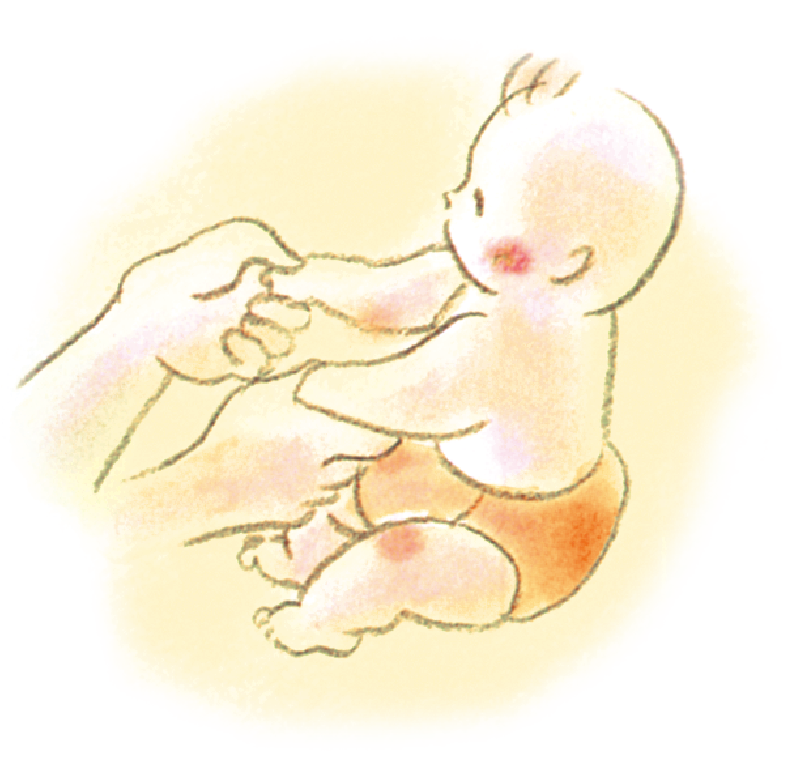

How to support your baby's hands
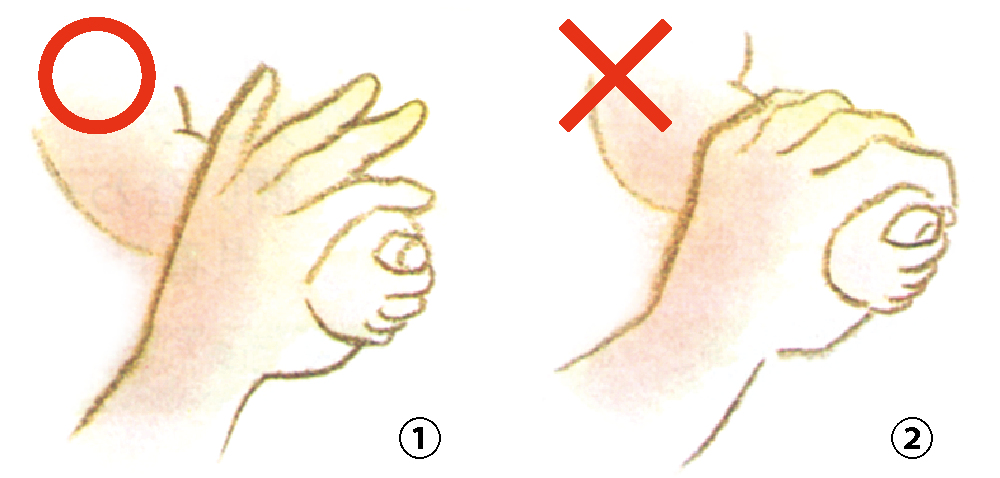
Let your baby grasp your thumb, with your other fingers resting lightly on their wrist. Avoid ①. Do not grab the arms ②.
How to support your baby's feet
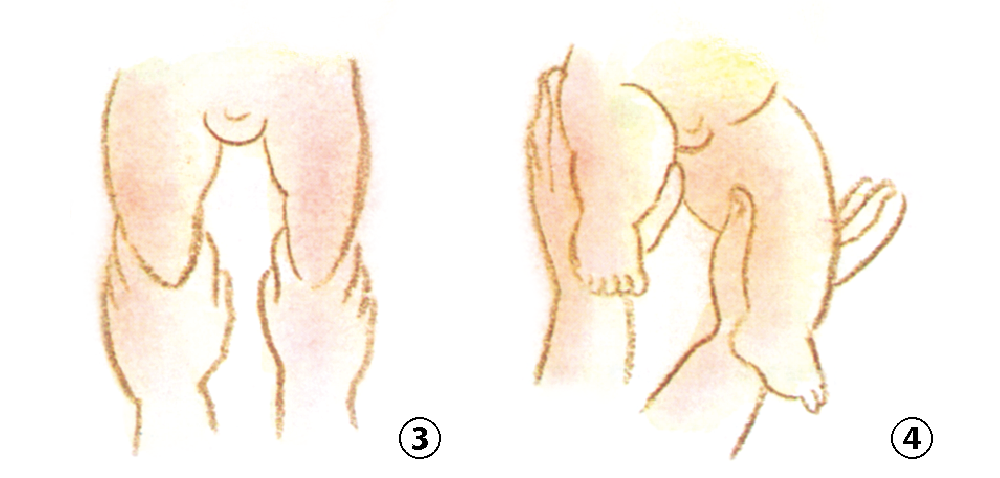
Gently hold the ankle between your index and middle fingers ③, and the back of the knee with your thumb and index finger ④.Avoid abrupt arm pulls or excessive leg stretching to prevent stress on elbows and hips.
FAQ
QMy baby is 15 days old and the face is still yellow. The baby is drinking a lot of breast milk and is doing well, but should I be concerned if this continues?
APhysiological jaundice is common in newborns, but if jaundice is severe, it could be due to blood type incompatibility or congenital biliary obstruction, which necessitates medical attention. Please consult with a healthcare professional.
Breastfeeding can sometimes prolong mild jaundice due to hormones in the milk.
If your baby appears healthy otherwise, the jaundice is likely related to breastfeeding and should naturally resolve about a month after birth without discontinuing breastfeeding.
QI'm worried because my baby doesn't seem to be gaining weight. The baby appears to be doing well, but maybe it's not getting enough breast milk?
AIt's natural for a baby's weight to fluctuate based on feeding and bowel movements. Daily weight monitoring isn’t necessary; once every 5 to 7 days is sufficient.
Weight gain may be slow initially as both mother and baby adjust to breastfeeding. If your baby seems happy and active, there's likely no issue. However, if you're concerned about insufficient breast milk, consider discussing supplementation options with a healthcare provider at your baby’s 1-month checkup.
QHe's only 2 weeks old, but I'm worried because he cries all the time. Is there something wrong with it? I couldn't sleep at night and was so tired.
ABabies cry for various reasons, such as insufficient feeding leading to hunger, discomfort from not burping after feeds, wet diapers, being overdressed causing them to sweat, or feeling too cold due to air conditioning.
Carefully observe your baby to identify if these issues are causing distress.
Monitoring your baby's weight gain is a useful indicator of whether they are receiving enough breast milk. Ensure proper burping techniques post-feeding to alleviate discomfort.
Growth Milestones
●Up to about 1 month
Babies typically experience cycles of sleeping and waking around the clock.

●1-2 months
You'll notice an increase in wakefulness during the day, with more sleep at night. Babies start to focus intently on faces and objects and respond to voices or rocking motions. Physical activity increases, including slight head lifting during tummy time.

Vaccine (immunization) debut
Begin vaccinations as your child reaches 2 months old.
●3-4 months
Your baby may start to laugh out loud in response to sounds or when being rocked. Once they can hold their neck steady, they'll begin to lift their head and shoulders while lying on their stomach.

Starting baby food

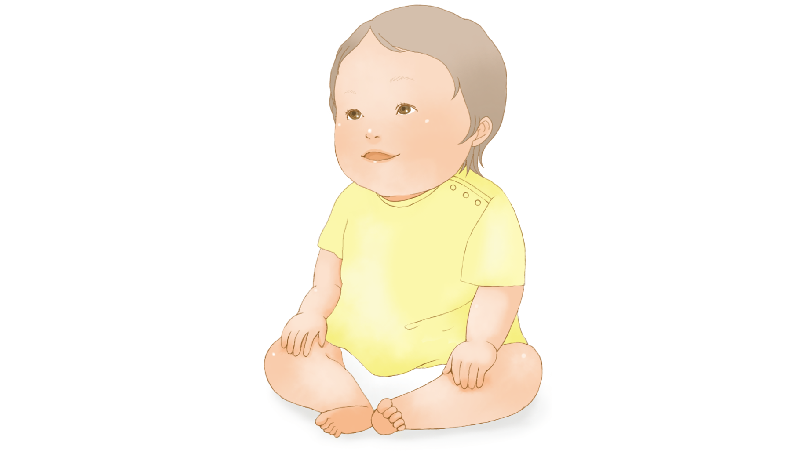
●5-6 months
Your baby might start rolling over during sleep and gradually begin sitting up. As they become proficient at rolling, they'll start to explore their surroundings, so vigilance is key.

●Around 7 months
Expect your baby to sit up steadily on their own.

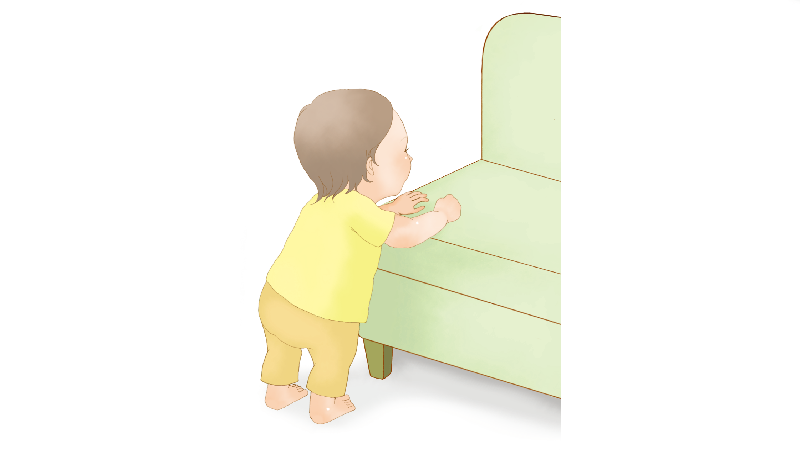
●Around 8 months
Crawling forward becomes the new milestone, increasing the need for supervision.

●9-10 months
Your baby will show interest in self-feeding.
●10-11 months
Your child may start to stand while holding onto something and take their first steps. Meal times become thrice a day, with established routines for waking up, napping, and bedtime.

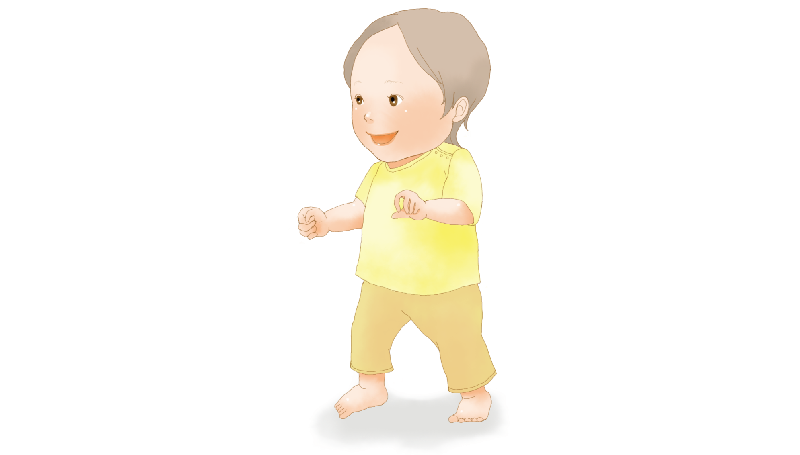
●Around 1 year old
By their first birthday, a child's weight typically triples from birth, and their height increases by about 1.5 times. Some children may begin walking around this time.

[Note] Baby growth varies from one individual to another. Not all babies develop at the same pace or reach milestones exactly as described.
